Nor again is there anyone who loves or pursues or desires to obtain pain of itself, because it is pain, but because occasionally circumstances occur in which toil and pain can procure him some great pleasure. To take a trivial example, which of us ever undertakes laborious physical exercise.
Some aspects of our health and vitality are governed by our genes and how our mother behaves during pregnancy, but many lifestyle factors, including fitness, diet and weight all impact on our ability to live a long and healthy life.
Start young
Even before we are born, our health can be affected by the lifestyle choices our mother makes. Studies have shown that if an expectant mother is highly stressed this may impact on their baby, leaving them less able to handle stress later in life.
Heavy drinking during pregnancy can lead to foetal alcohol syndrome in babies – which can cause a life-long learning disability as well as physical problems. Smoking can also affect their development. Research also suggests a pregnant woman’s diet can increase her child’s risk of obesity by changing the unborn baby’s DNA.
Having a happy childhood may boost longevity, as a study suggests those who are unhappy in their youth have a greater risk of heart disease as adults.
Getting outdoors is also key, as sunlight is an important source of vitamin D. At present one in four children are deficient in this vitamin, which is needed for building strong and healthy bones. Vitamin D helps our bodies to absorb calcium and phosphorus from our diets.
Is life expectancy in our DNA? The caps at the end of chromosomes called telomeres could indicate the life expectancy of a young bird
Benefits of exercise
The pressures of home and family life can make it feel like there’s little time to exercise. Aside from weight loss, there is a lot to gain from exercise and it can make a huge difference to staying healthy:
- Exercise means a healthier heart because it reduces several cardiovascular risks, including high blood pressure and heart disease
- Being physically active can bolster good mental health and help you manage stress, anxiety and even depression.
- Regular exercise can help you achieve and maintain an ideal weight and reduce the risk of diabetes
- Weight bearing exercise, such as running is especially good in promoting bone density and protecting against osteoporosis – which is when bones become thin, weak and break easily
Bone health
In childhood our bones are strong and, if they break, they usually repair quickly. When we get older this process slows down and our joints can become weak and fragile.
We begin to lose bone density from our mid-30s, which is a normal part of ageing.
According to Dr. Dee from Healing Hands Chiropractic, lifestyle factors such as having a calcium-rich diet and exercising frequently can keep bones healthy and minimise the risk of fractures. Sunlight exposure is also crucial to up levels of vitamin D.
The Okinawa – Japanese fishermen who live long lives
- Okinawa has around four times more centenarians than Britain
- Their most significant cultural tradition is known as hara hachi bu, which translated means eat until you’re only 80% full
- In a typical day they consume around 1,200 calories – about 20% less than most people in the UK
- The towns where people live the longest
- What is the ultimate healthy meal?
We all know that friends are important for a happy life, but it has recently been discovered that friendship could actually help us live longer.
Studies on loneliness have found that social isolation is associated with a higher rate of death in older people and loneliness is the “hidden killer” of the elderly.
In a similar vein, research has shown that people who marry live longer than those who are single. The researchers believe that those who marry have better social support networks, minimising the risk of isolation.
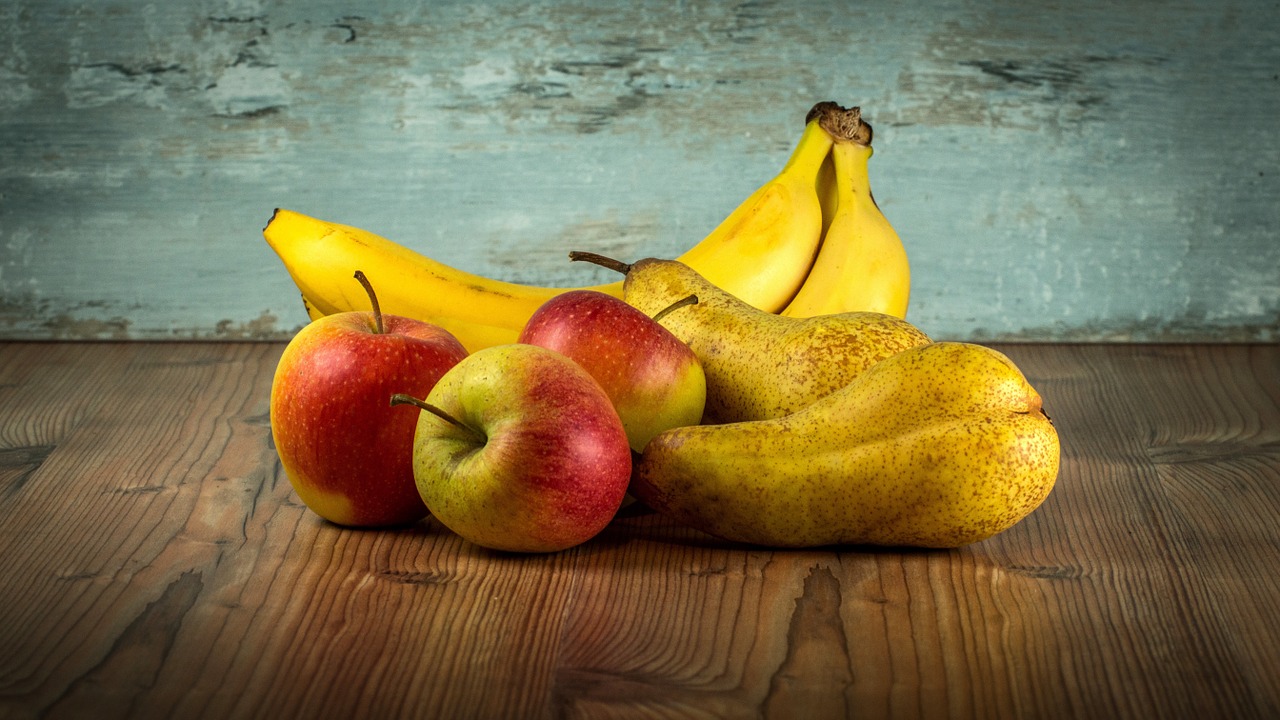
Avoiding junk food
The Chiropractors in Centurion say that a good diet is central to overall good health, though avoiding certain foods and drinks may help prolong your life. Eating too much high-calorie food rich in simple carbohydrates (sugars) or fat could lead to weight gain or obesity.
NICE’s Professor Mike Kelly discusses the dangers of trans-fats
Some fats are known to be particularly bad for you. Trans-fats, made from hydrogenated vegetable oil, can be found in margarine, biscuits, cakes and fast food. It can raise the level of our ‘bad’ cholesterol, significantly increasing the risk of atherosclerosis which blocks arteries, leading to heart disease and stroke.
NHS watchdog NICE has called for them to be banned in food.
Reducing salt intake is also important to keep your heart healthy, as eating too much salt could lead to high blood pressure – which in turn may lead to heart failure, stroke and other complications.
Drinking too much alcohol can also have devastating effects on our health – not only can it leave us with a hangover the next day, but drinking more than the recommended intake on a regular basis can also cause long-term damage to the body’s internal organs. Chronic misuse is one of the major causes of liver disease.
Ditching cigarettes is also key. Smoking increases your risk of more than 50 serious health conditions. It causes about 90% of lung cancers, damages your heart and your blood circulation, worsens respiratory conditions and affects fertility.
And finally, is it all in our DNA?
Although there are measures we can take to help us live a long and healthy life, there may be an element of luck involved – depending on our DNA.
Much research into ageing has been focused on the role of telomeres. These are the protective tips found at the end of chromosomes, sometimes likened to the tips of shoelaces. Their role is to safeguard the end of the chromosome and to prevent the loss of genetic information during cell division.
Each time our cells divide, the tips of our telomeres become shorter. Eventually they become so short, they stop our cells dividing which means the cells die, which is how we age.
Studies have revealed that longer telomeres have been linked to a longer lifespan, while shorter telomeres have been linked diseases such as heart disease and dementia. Longer telomeres can also be inherited by the next generation.

















































































































COMMENTS